|
Procedures for Obtaining a
Patent Right
|
|
|
|
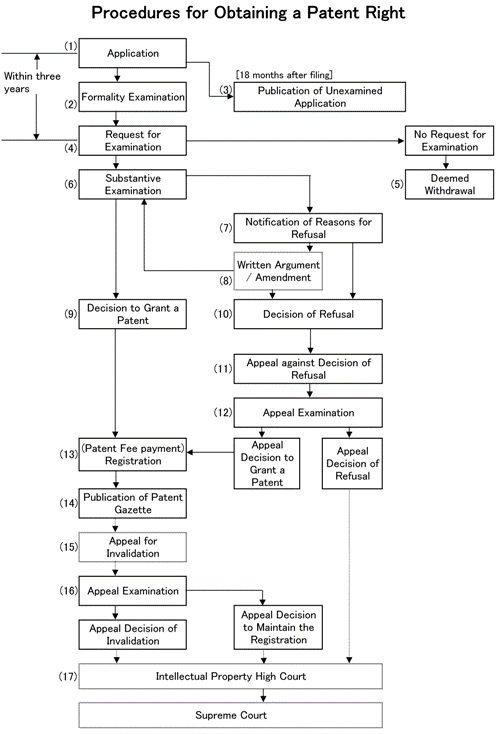
In order to obtain a patent
right, you must apply to the Japan Patent Office and go through examinations
to determine whether the application fulfills all the necessary requirements.
The JPO, which
examines all applications from around the world, takes precautionary measures
before ultimately granting any patent right. These involve exchange of
documents with the applicant to determine which claims, if any, are entitled
to be patented. The whole procedure from filing to registration is shown in
the flow chart below.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
Application
|
|
No matter how good an invention
may be, a patent right naturally cannot be obtained unless it is applied for.
An application requires that one fills out the forms prescribed in the
relevant ordinances and submit them to the JPO.
Japan
has adopted the first-to-file system, i.e. the principle that where two
parties apply for a patent for the same invention, the first party to file
will be granted the patent. Accordingly, it is advisable to file as soon as
possible after the invention. It is also advisable not to make the invention
public before filing a patent application.
|
|
(2)
|
Formality Examination
|
|
An application document
submitted to the JPO will be checked to see whether it fulfills the necessary
procedural and formal requirements. An invitation to correct will be made
where necessary documents are missing or required sections have not been
filled in.
|
|
(3)
|
Publication of Unexamined
Application
|
|
The JPO will publish the content
of an application in the Official Gazette after 18 months have elapsed from
the date of filing.
|
|
(4)
|
Request for Examination
|
|
Patent applications are not
necessarily examined. An examination will be carried out only for the
application for which the applicant or a third party has filed a request for
examination and paid the examination fees.
|
|
(5)
|
Deemed Withdrawal (No Request
for Examination)
|
|
Any application for which a
request for examination has not been filed within a period of *three years
from filing date will automatically be regarded as withdrawal and cannot be
patented thereafter.
|
|
(6)
|
Substantive Examination
|
|
An examination will be carried
out by an examiner of the JPO, who will decide whether or not the claimed
invention should be patented. The examiner firstly checks whether the
application fulfills requirements prescribed by law, i.e., whether or not
there are any reasons for refusal. These requirements include the following:
|
|
1.
|
Whether the claimed invention
is based on a technical idea which utilizes a law of nature,
|
|
2.
|
Whether it has any industrial
applicability,
|
|
3.
|
Whether the technical idea
existed before the filing of the current application,
|
|
4.
|
Whether the claimed invention
could have been easily invented by a person skilled in the art,
|
|
5.
|
Whether the application is the
first to file,
|
|
6.
|
Whether the claimed invention
is liable to contravene public order and morality, and
|
|
7.
|
Whether the descriptions in
the specification conform exactly with the requirements for patentability.
|
|
|
(7)
|
Notification of Reasons for
Refusal
|
|
If the examiner finds reasons
for refusal, a notification to this result will be sent to the applicant.
|
|
(8)
|
Written Argument / Amendment
|
|
An applicant who has received
the notification of reasons for refusal shall be given an opportunity to
submit either a written argument claiming that the invention differs from the
prior art to which the notification of reasons for refusal refers, or an amendment
of the claims in the case that this would nullify the reasons for refusal.
|
|
(9)
|
Decision to Grant a Patent
|
|
As a result of the examination,
the examiner will make a decision to grant a patent as the final assessment
of the examination stage if no reasons for refusal have been found. The
examiner will also make the same decision if the reasons for refusal have
been eliminated by an argument or amendment.
|
|
(10)
|
Decision of Refusal
|
|
On the other hand, if the
examiner judges that the reasons for refusal have not been eliminated, a
decision of refusal (the final assessment of the examination stage) will be
made.
|
|
(11)
|
Appeal against Decision of
Refusal
|
|
When dissatisfaction is in the
decision of refusal of the examiner, the applicant may appeal against the
decision of refusal.
|
|
(12)
|
Appeal Examination (against
Decision of Refusal)
|
|
The appeal examination against
the decision of refusal is performed by a collegial body of three or five
appeal examiners.
Decision of the appeal examiners is called an appeal decision.
When it is judged as a result of appeal examination that the reasons for
refusal was solved, an appeal decision to grant a patent is performed, and
when the appeal examiners judge that the reasons cannot be canceled and the
patent cannot be registered, an appeal decision of refusal is performed.
|
|
(13)
|
Registration (Patent Fee
Payment)
|
|
Provided that the applicant pays
the patent fee, once the decision to grant a patent has been made the patent
right will come into effect as it is entered in the Patent Register. At the
same time, the invention acquires a patent number. After a patent is
registered, a certificate of patent will be sent to the applicant.
|
|
(14)
|
Publication of Patent Gazette
|
|
The contents of the patent right
entered in the Register will be published in the Patent Gazette.
|
|
(15)
|
Appeal for Invalidation
|
|
Even after a patent is
registered, any person may appeal for invalidation of the patent if it has a
flaw.
|
|
(16)
|
Appeal Examination
(Invalidation)
|
|
An appeal examination of
invalidation is carried out by a collegial body of three or five appeal
examiners.
If the appeal examiners judge that there is no flaw in the decision to grant
a patent, they will make a decision to maintain the patent. If however they
judge that the decision to grant was flawed, they will make a decision to
invalid the patent right.
|
|
(17)
|
Intellectual Property High Court
|
|
An applicant who is dissatisfied
with an appeal decision of refusal of an appeal against decision of refusal,
and an interested party who is dissatisfied with an appeal decision of
invalidation or maintenance, may appeal to the Intellectual Property High
Court.
|
|
|
(Note)
|
|
•
|
The revised time limit is to
be applied for patent applications filed after October 1, 2001.
|
|
•
|
To the patent applications
filed before September 30, 2001, the time limit of seven years from the
filing date is to be applied.
|
|
•
|
As for the details, click for
‘Revision of the time limit for submitting a request for examination.’
|
|